JEE Main Session 1 Physics 30 Most Expected Questions 2025: Candidates planning to appear for JEE Main Session 1 from January 22 to 30, 2025 can go through the details on the Physics section here. They can reference the JEE Main Session 1 Physics 30 Most Expected Questions 2025 here. The provided questions have been repeated based on the previous year's trends. Moreover, these questions carry a high weight, increasing the chances of candidates scoring well. The JEE Main Session 1 Physics 30 Most Expected Questions 2025 are available here for the students to go through.
Also Read |
JEE Main Important Links |
JEE Main Session 1 Physics 30 Most Expected Questions 2025
Candidates can go through the JEE Main Session 1 Physics 30 Most Expected Questions 2025 below.
Q1. . Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and carrying equal charges in them repel each other with a force F when kept apart at some distance. A third spherical con- ductor having same radius as that of B but uncharged, is brought in contact with B, then brought in contact with C, and finally removed away from both. The new force of repulsion between B and C is
- F/4
- 3F/4
- F/8
- 3F/8
Q2. A block of mass ar is placed on a smooth fixed sphere of radius R. It slides when pushed slightly. At what vertical distance, from the top, will it leave the sphere?
- R/4
- R/3
- R/2
- R
Q3. The magnetic field associated with a light wave is given, at the origin, by B [sin(3.14×10)er+sin(6.28×10). If this light falls on a sliver plate having a work function of 4.7 eV, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons? ) (c3x10msh=6.6×10J
- 6.82 eV
- 12.5 eV
- 8.52 eV
- 7.72V
Q4. Three particles, each of mass M, are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side length a. The only forces acting on the particles are their mutual gravitational forces. It is desired that each particle moves in a circle while maintaining- ing the original mutual separation a, find the period of revolution.
- * pi * sqrt((a ^ 3)/(3GM))
- 2* pi * sqrt((a ^ 3)/(3GM))
- sqrt ((alpha ^ 3)/(3GM))
- * 5pi * sqrt((alpha ^ 3)/(3GM))
Q5. Figure shows a polytropic process (PI constant) for an ideal gas. The work done by the gas in process AB is
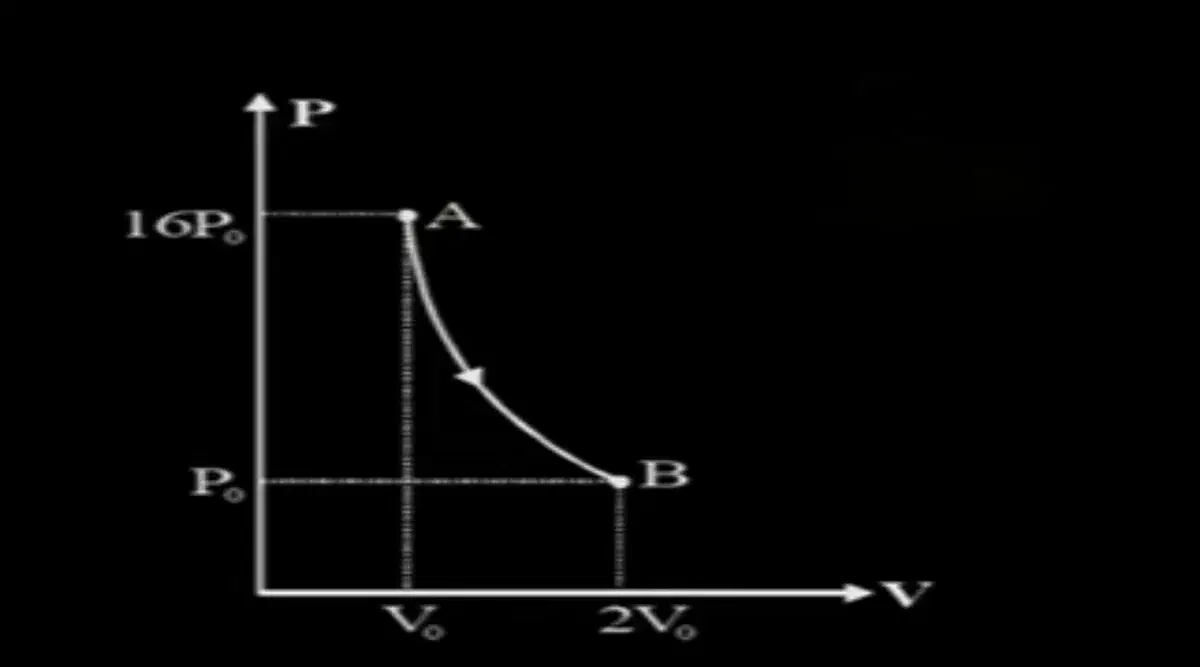
Q6. For the circuit shown, with R_{1} = 1Omega R_{2} = 2Omega E2F and EE41, the potential difference between the points "a" and "" is approximately (in V)
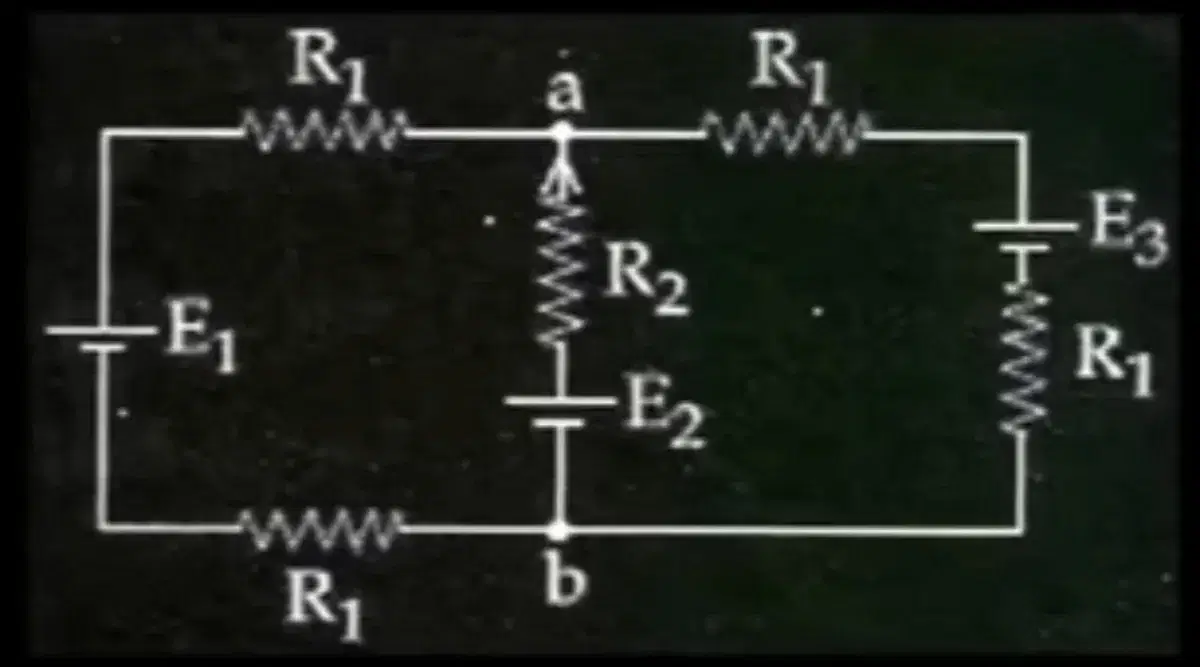
- 2.7
- 2.3
- 3.7
- 33
Q7. A capacitor is connected to a 20 V battery through a resistance of 102. It is found that the potential difference across the capacitor rises to 2 V in 1 us The capacitance of the capacitor is. Given: ln(10/9) = 0.105
- 9.52
- 0.95
- 0,105
- 1.85
Q8. A bullet of mass 0.01 kg and horizontal speed 100 mm strikes a block of wood of mass 0.49 kg and instantly comes to rest w.rt. Block. The block is suspended from the ceiling using thin wires. If the height (in cm) to which the block rises is 2.5p, the find the value of p. (take g=10m/s)
Q9. To get output '1' at R, for the given logic gate circuit, the input values must be
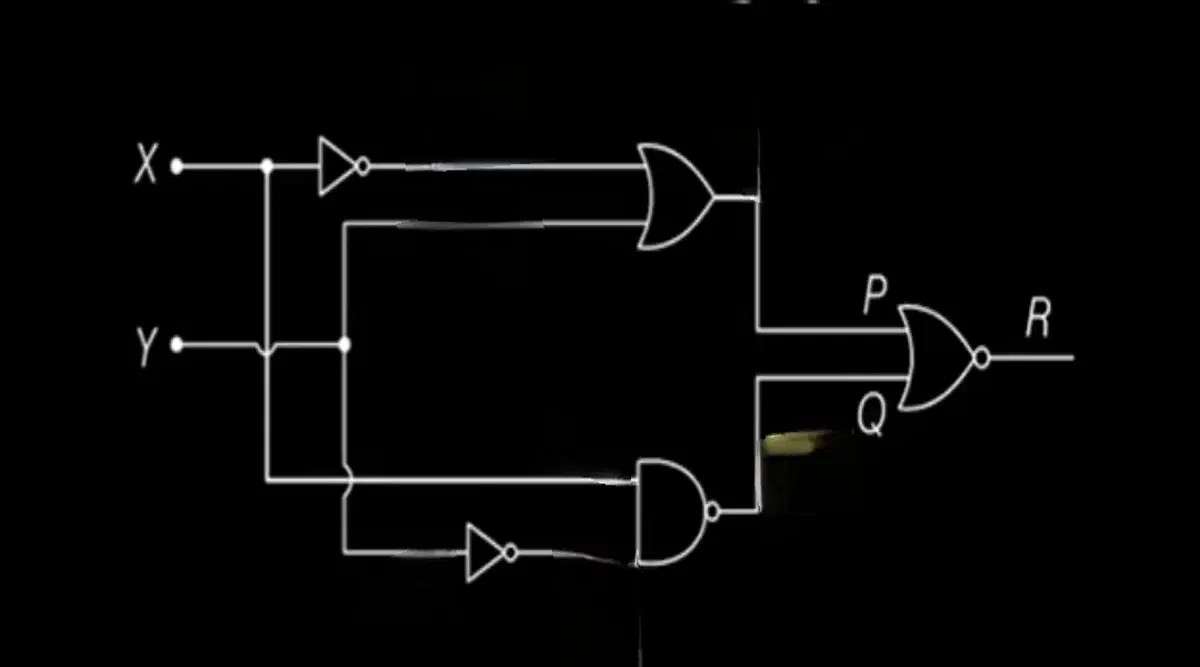
- X = 0 Y = 0
- X = 1 Y = 0
- X = 1 Y = 1 X
- X = 0 Y = 1
Q10. A rubber pipe of density 1.5×103 N/m² and Young's modulus 5x106 N/m² is suspended from the roof. The length of the pipe is 8 m. What will be the change in length due to its own weight
- 9.6 m
- 9.6×10³ m
- 19.2x102 m
- 9.6×10-2 m
Q11. On a smooth inclined plane, a body of mass M is attached between two springs. The other ends of the springs are fixed to firm supports. If each spring has force constant K, the period of oscillation of the body (assuming the spring is massless) is?
Q12. The interference pattern is obtained with two coherent light sources of intensity ratio 4:1. And the ratio Imax + Imin is 5 Then, the value of x Imax - Imin X will be equal to
- 3
- 4
- 2
- 1
Q13. Two lighter nuclei combine to form a comparatively heavier nucleus by the relation given below: so X+XY The binding energies per nucleon X and Y are 1.1 MeV and 7.6 MeV respectively. The energy released in this process is.
Q14. A person is standing on a weighing machine placed on the floor of an elevator. The motion of the elevator is shown in the adjacent diagram. The maximum and the minimum weights recorded are 66 kg and 57 kg. The true weight of the person is [Take g = 10 m/s².]
Q15. A body is projected from the ground at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. Its velocity after 2s is 20 ms¹. The maximum height reached by the body during its motion is m. (use g = 10ms-²)
Q16. A capacitor C is fully charged with voltage V. After disconnecting the voltage source, it is connected in parallel with another uncharged capacitor of capacitance C/2. The energy loss in the process after the charge is distributed between the two capacitors is
- 1/6C2 V0
- 1/2C2 V0
- 1/3C2 V0
- 1/4C2 V0
Q17. A simple pendulum is being used to determine the value of gravitational acceleration g at a certain place. The length of the pendulum is 25.0 cm and a stopwatch with 1 s resolution measures the time taken for 40 oscillations to be 50 s. The accuracy in g is
- 2.40%
- 5.40%
- 4.40%
- 3.40%
Q18. The value of the acceleration due to gravity is g, at a height hR/2 (R-radius of the earth) from the surface of the earth. It is again equal to g, at a depth d below the surface of the earth. The ratio (d/R) equals
- 7/9
- 4/9
- 1/3
- 5/9
Q19. A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process ABCA as shown in the figure. It absorbs, 40 J of heat during part AB, no heat during BC, and rejects 60J of heat during CA. A work 50J is done on the gas during part BC. The internal energy of the gas at A is 1560J. The work done by the gas during the part CA is: 28-2
- 20 J
- 30 J
- -30J 4.6K
- -60 J
Q20. The one division of the main scale of Vernier calipers reads 1 mm and 10 divisions of the Vernier scale are equal to the 9 divisions on the main scale. When the two jaws of the instrument touch each other the zero of the Vernier lies to the right of the zero of the main scale and its fourth division coincides with a main scale division. When a spherical bob is tightly placed between the two jaws, the zero of the Vernier scale lies between 4.1 cm and 4.2 cm, and the 6th Vernier division coincides with a main scale division. The diameter of the bob will be 102 cm.
Q21. A nucleus of mass M at rest splits into two parts having masses M/3 and 2M/3(M less than M)
The ratio of de Broglie wavelength of two parts will be:
- 1:2
- 2:1
- 1:1
- 2:3
Q22. Consider two uniform discs of the same thickness and different radii R, Rand R, OR made of the same material. If the ratio of their moments of inertia / and 1, respectively, about their axes is 1:1, 1: 16 then the value of a is
- √2
- 2
- 4
- 2√2
Q23. An electron is moving along +x direction with a velocity of 6 x 106 ms¹. It enters a region of uniform electric field of 300 V/cm pointing along +y direction. The magnitude and direction of the magnetic field set up in this region such that the electron keeps moving along the x direction will be
- 5×10-3 T, along +z direction
- 3×10-4T, along-z direction
- 3×10-4T, along +z direction
- 5×103T, along -z direction
Q24. An unpolarised light beam of it. 21o is passed through a polaroid P and then through another polaroid Q which is oriented in such a way that its passing axis makes an angle of 30° relative to that of P. The intensity of the emergent light is
Q25. An unpolarised light beam of it. 21o is passed through a polaroid P and then through another polaroid Q which is oriented in such a way that its passing axis makes an angle of 30° relative to that of P. The intensity of the emergent light is
Q26. In a series LCR circuit, R = 2002 and the voltage and frequency of the main supply are 220 V and 50 Hz respectively. On taking out the capacitance from the circuit, the current lags behind the voltage by 30°. On taking out the inductor from the circuit the current leads the voltage by 30°. The power (in W) dissipated in the LCR circuit is
Q27. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed in front of a convex mirror with the principal axis coinciding with each other. The distance between the lens and mirror is 10 cm. A point object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of 60 cm from the convex lens. The image formed by combination coincides with the object itself. The focal length of the convex mirror is cm.
Q28. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed in front of a convex mirror with the principal axis coinciding with each other. The distance between the lens and mirror is 10 cm. A point object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of 60 cm from the convex lens. The image formed by combination coincides with the object itself. The focal length of the convex mirror is cm.
Q29. A block of ice of mass 120 g at temperature 0°C is put in 300 gm of water at 25°C. The xg of ice melts as the temperature of the water reaches 0°C. The value of x is [Use: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 Jkg-K-¹, Latent heat of ice = 3.5 × 105 Jkg¹]
Q30. Two concentric circular coils, C, and C₂, are placed in the XY plane. C₁ has 500 turns, and a radius of 1 cm, C₂ has 200 turns and a radius of 20 cm. C carries a time-dependent current I(1) = 2 (5f-21+3) A where / is in s. The emf induced in C, (in mV), at the instant 1 = 1s is 4/x. The value of x is
JEE Main Session 1 Important Links |
Also check |
JEE Main Expected Attempt vs Percentile Marks |

POST YOUR COMMENT